Sign a PDF with a Certificate on Android
PSPDFKit enables signing both existing signature form elements and documents without a signature form element.

If you want to use the Digital Signatures component, make sure it’s included in your license. Please contact Sales for more information.
Approval and Certification Signatures
PDF documents mainly support two types of digital signatures: approval signatures, and certification signatures. Approval signatures are used to indicate that a signer agrees with or acknowledges the contents of a document. A single document can contain multiple approval signatures. Meanwhile, certification signatures restrict the kind of changes that can be applied to a document once it’s signed. A PDF document only allows one certification signature. PSPDFKit provides support for approval signatures. For certification signatures, contact us on Support.
Creating a Digital Signature
Adding a digital signature on a PDF document is both reliable proof of the document’s origin and protection against modification by third parties.
To create a digital signature, you need two things.
-
First, you need an X509 certificate that contains your public key and your signer information. PSPDFKit supports PEM-encoded and DER-encoded X509 certificates, as well as DER-encoded PKCS#7 certificates. You can check the encoding of a certificate file by using the OpenSSL command-line tool as follows:
openssl pkcs7 -noout -text -print_certs -in example.p7b
The above command will print an error message if “example.p7b” is not a PEM-encoded PKCS#7 certificate or certificate chain.
To verify if a PKCS#7 certificate file is correctly DER encoded, you can use this command instead:
openssl pkcs7 -inform der -noout -text -print_certs -in example.p7b
The above command will print an error message if “example.p7b” is not a DER-encoded PKCS#7 certificate or certificate chain.
-
Second, you need your private key.
Signing Process
The signing process produces the signature by encrypting the message digest from the PDF file with a private key. The certificate with its public key is added to the signature and saved in the PDF file. The SigningManager class allows signing of documents by adding a digital signature to a SignatureFormField. It allows both computation and saving of digital signatures to a definable output file.
PSPDFKit ships with two ways to sign your documents.
-
The simplest approach takes a
PrivateKeythat was loaded by your app and uses it to sign a document directly:
val signerOptions = SignerOptions.Builder(signatureFormField, outputFileUri) .setPrivateKey(key) .build() SigningManager.signDocument(context = context, signerOptions = signerOptions, type = digitalSignatureType, onFailure = { // Handle signing errors here. } ) { // The document was successfully signed! val signedDocument = Uri.fromFile(outputFile) }
-
Another approach loads the signing certificates from a PKCS#12 file (usually with the
.p12file extension) and provides you with the flexibility to sign the byte array yourself:
val signerOptions = SignerOptions.Builder(signatureFormFields, outputFileUri) .setCertificates(getX509Certificates()) .build() SigningManager.signDocument(context = context, signerOptions = signerOptions, type = digitalSignatureType, customSigning = { data, hashAlgorithm -> // Here you're manually signing `ByteArray` with the provided `hashAlgorithm` and private key. This is a mandatory step if // the customer doesn't provide a private key in `SignerOptions`. data.signData(key, hashAlgorithm) }, onFailure = { // Handle signing errors here. } ) { // The document was successfully signed! val signedDocument = Uri.fromFile(outputFile) }

For an interactive example of digital signatures, check out
DigitalSignatureExampleandManualSigningExamplein the Catalog app.
Editing a Digitally Signed Document
When displaying digitally signed documents, PSPDFKit will allow annotation editing unless a DocMDP transform method is specified under the TransformMethod key of the signature information dictionary. When PSPDFKit is used for the signing process, this method is never set, which means annotation editing remains enabled.
Signing a PDF Multiple Times
One of the prominent features of digital signatures in PDFs is the possibility for an unlimited number of signers. This feature is especially useful for multi-party contracts, legal documents, and other formal agreements where more than two parties are involved. Each of these parties can append their signature to a document, ensuring it carries the approvals needed to make it legally binding.
Each time a signature is added to a PDF, an extra layer of security is included with the document. This increases the integrity of the document up to the point of each signature, a feature known as “non-repudiation.” In simpler terms, non-repudiation ensures that a party involved in a contract or agreement cannot deny the authenticity of their electronic signature, as it serves as a proof of consent or approval.
Each digital signature generates a version, or revision, of the document. Hence, a document can house multiple revisions if it has been signed repeatedly with approval signatures (see Approval and Certification Signatures). When third-party software such as Adobe Acrobat verifies a document with several digital signatures, it ensures each revision only includes specific permissible modifications. Typically, new revisions allow the addition of notes, filling out form fields, or placing subsequent signatures on the document. However, alterations like page modifications will invalidate the digital signature.
Here’s a diagram that shows how revisions work in a PDF document.
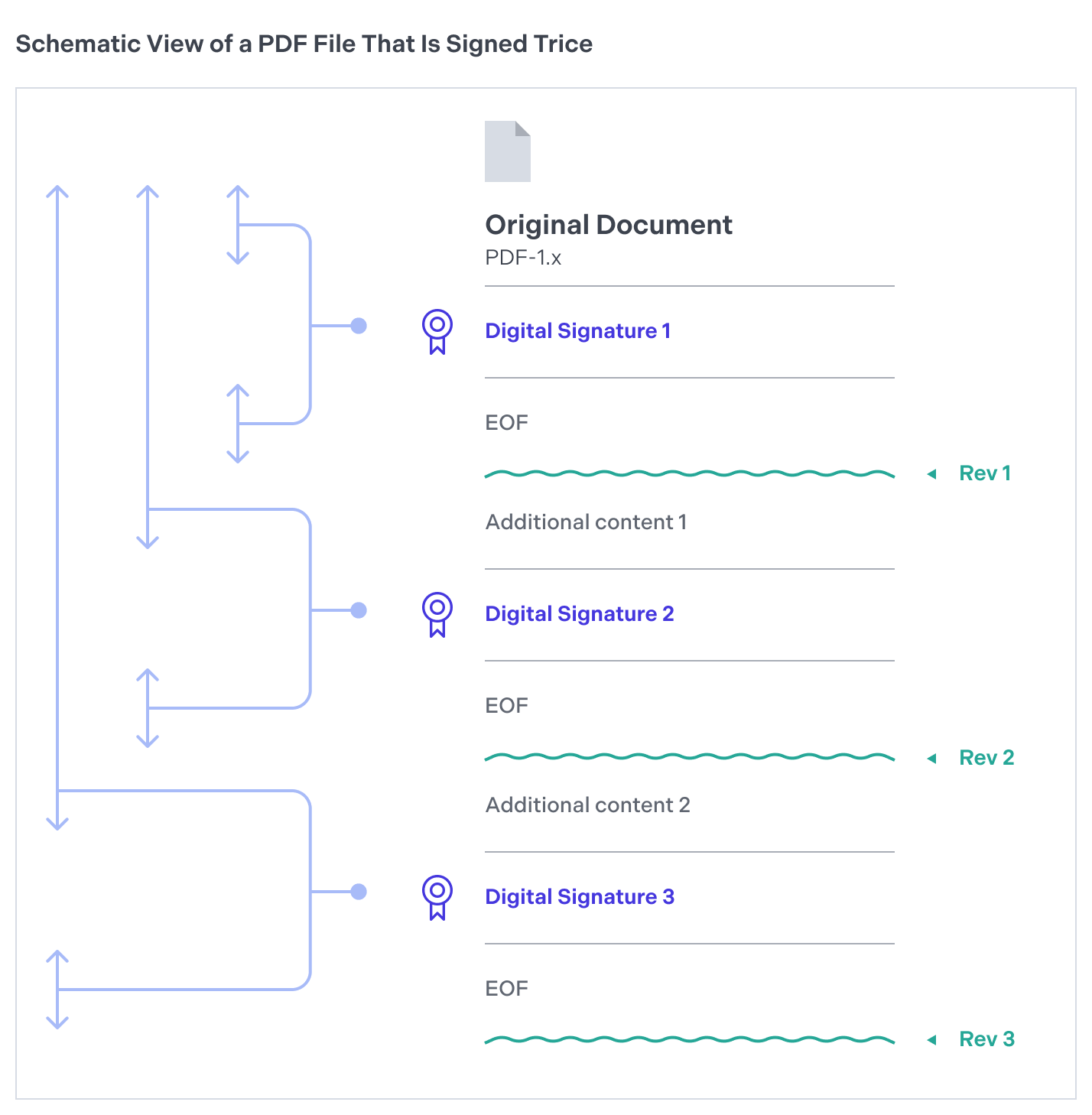
Digital PDF signatures, which can include time stamps, provide a comprehensive audit trail detailing when each party reviewed and consented to the document’s content. This chronological record is particularly beneficial in compliance scenarios, as it presents an irrefutable timeline of when approvals were procured.
If you wish to sign a document again after executing permissible changes (e.g. filling in a form), add a new signature form field by following the steps outlined in the Add a Signature Field section, and then complete the signing process by following the guidelines provided in the Signing a PDF section.
Note that each signature added will slightly increase the file size. This can impact storage and sharing capabilities of the document, especially when there are a large number of signatures appended. However, considering the security that digital signatures provide, it’s usually considered a small price to pay.
Removing a Digital Signature
If you want to remove a signature, access the signed SignatureFormField and call removeSignature() or removeSignatureAsync(). This will remove the DigitalSignatureInfo from the given SignatureFormField.